Spinner
Menu
About EAA
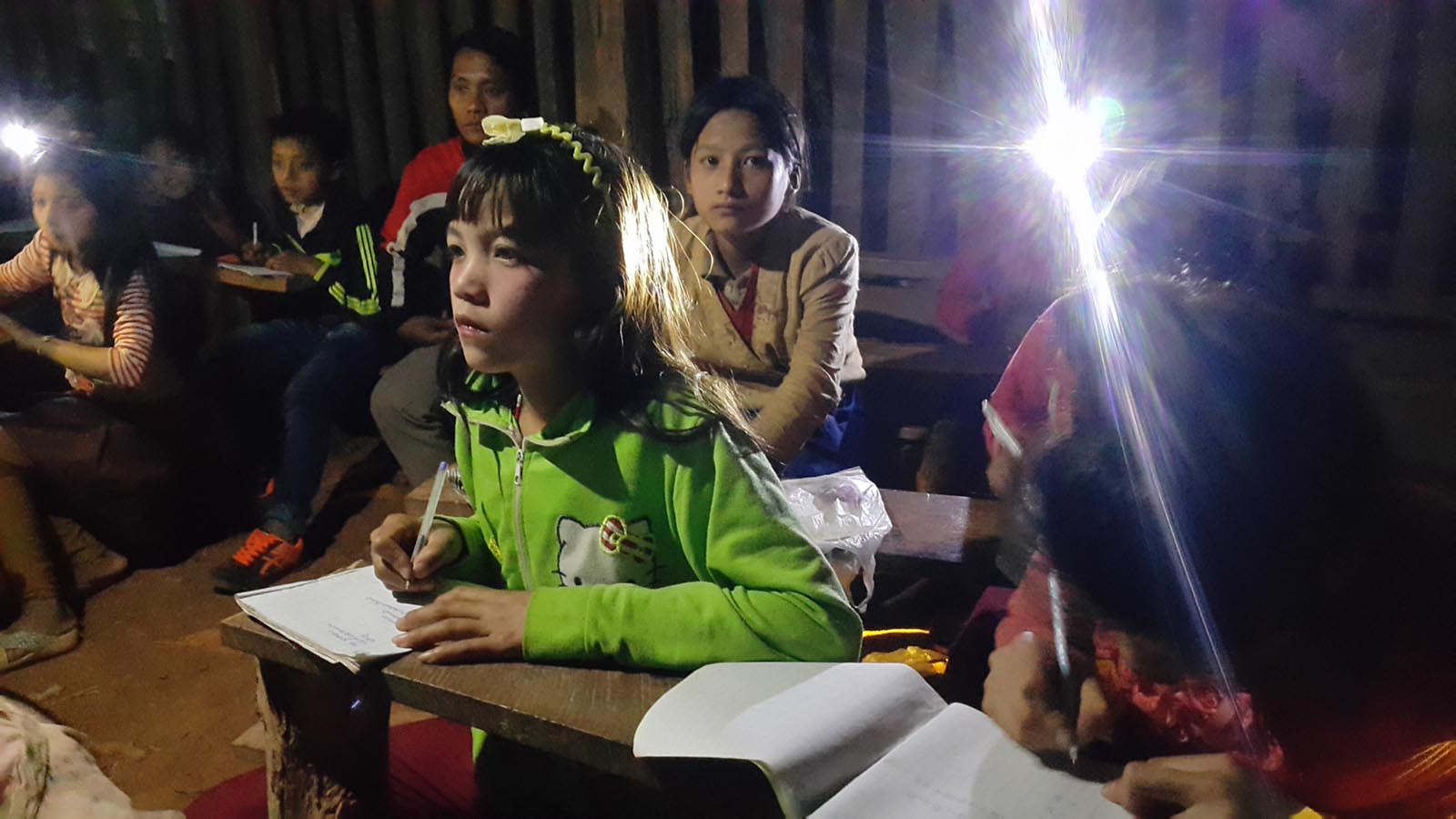
Opening up a world of education
Children love to learn. If they are denied access to knowledge, we also deny them the opportunity to change their lives for the better.
Explore EAA Projects
Disclaimer: This map is provided to facilitate the general location of the EAA supported projects. EAA does not have an official position regarding boundaries of or disputed boundaries between countries.
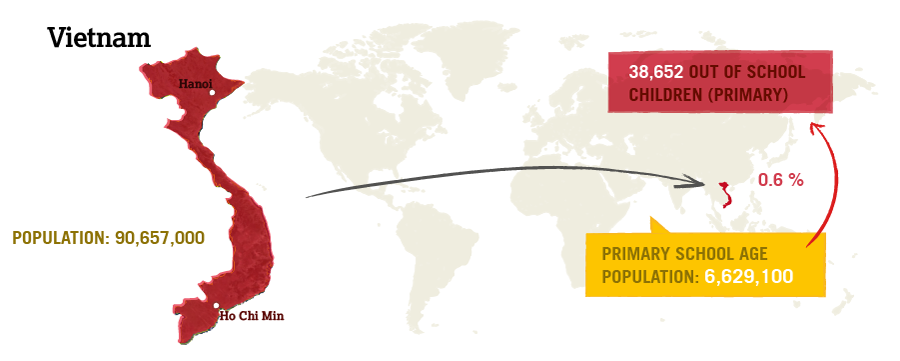
Vietnam

Main Barriers to Education
- War and conflicts
- Poverty
- Economic and Financial difficulties
- Child Labour
- Poor Quality Teaching
- Distance to school and Inadequate school infrastructure
- Cultural customs, traditions and perceptions of the value of educating girls
Economic growth in Vietnam has averaged a strong 6.4% each year for the past decade, this has begun to slow in recent times, as is similar with the country’s GDP, which in 2013 was 5.4%, and which is also projected to slow this year. Inflation in Vietnam plummeted from 23% in 2011 to 4.2% in 2014, therefore stabilizing their economy.
Vietnam was not always so economically fortunate; in 1986 the government introduced reforms that would lift this country from being one of the poorest in the world, to being a lower middle income country within a quarter of a century. In the 1990’s more than 60% of this country’s population were in poverty, today, this amount is under 10% and in the same time frame, mean income for the bottom 40% of the Vietnamese population increased by an annual average of 9% according to the World Bank.
Vietnam has already met four of its ten millennium development goals and is on target to meet three more by 2015. This country has made impressive strides toward ensuring all children have access to a quality education. With 96% of six to 11-year-olds enrolled in primary school.
SOURCES: WORLDBANK, WORLDBANK RESOURCES, UNICEF, EAST ASIA FORUM
Partners
Projects
Education Above All
P.O Box 34173
Doha - Qatar
Copyright © 2025 . All Rights Reserved